Unveiling the Mystery of Dark Tourism: An In-depth Analysis
The human mind is a curious entity, often drawn towards the unknown, the eerie, and the macabre. One such manifestation of this curiosity is the growing interest in dark tourism. It is a form of tourism involving visits to places associated with death, tragedy, or the seemingly macabre. From the somber Auschwitz concentration camps to the eerie corridors of Chernobyl, dark tourism is an emerging trend that is altering the conventional paradigms of travel.

A Brief History and Key Developments
Dark tourism, though a relatively new term, is not a novel concept. For centuries, humans have exhibited a morbid curiosity towards sites associated with death or tragedy. In the Middle Ages, pilgrims traveled to shrines of martyrs, while the Parisians of the 19th century flocked to witness public executions.
The term “dark tourism” was first coined in the late 1990s by two academics, John Lennon and Malcolm Foley. Over the years, this form of tourism has evolved, encompassing a wide range of sites—from battlefields and disaster zones to prisons and haunted houses. Today, dark tourism is a significant segment of the global tourism industry, reflecting the shifting dynamics of traveler interests.
Current Trends and Insights
The rise of dark tourism is influenced by several factors. The millennial and Gen Z travelers, driven by an urge to understand and empathize with the harsh realities of the past, are particularly drawn to these sites. The pervasive influence of social media and the desire for unique, offbeat experiences also contribute to this trend.
Increasingly, governments and tourism bodies are recognizing the potential of dark tourism. These sites offer an opportunity to educate visitors about historical events and their ramifications while encouraging reflection on societal issues.
The Impact of Dark Tourism
Dark tourism has a unique impact, offering an immersive, albeit somber, travel experience. It provides a stark contrast to the typical sun-and-sand vacations, challenging travelers to confront uncomfortable realities.
However, dark tourism also poses ethical dilemmas. The commercialization of tragedy and the risk of trivializing historical atrocities are contentious issues. It’s crucial for operators and visitors to approach these sites with sensitivity and respect for the lives and events they represent.
Practical Implications of Dark Tourism
The shift towards dark tourism impacts the travel industry at multiple levels. It expands the scope of tourism, opening up lesser-known destinations. It also encourages a more holistic approach to travel, blending education with exploration.
Travel agencies and operators need to carefully curate dark tourism experiences, ensuring they are informative and respectful, rather than exploitative. Visitor etiquette is also crucial to maintain the sanctity of these sites.
Fascinating Facts about Dark Tourism
-
The Aokigahara Forest in Japan, known as the “Suicide Forest,” is one of the most infamous dark tourism sites.
-
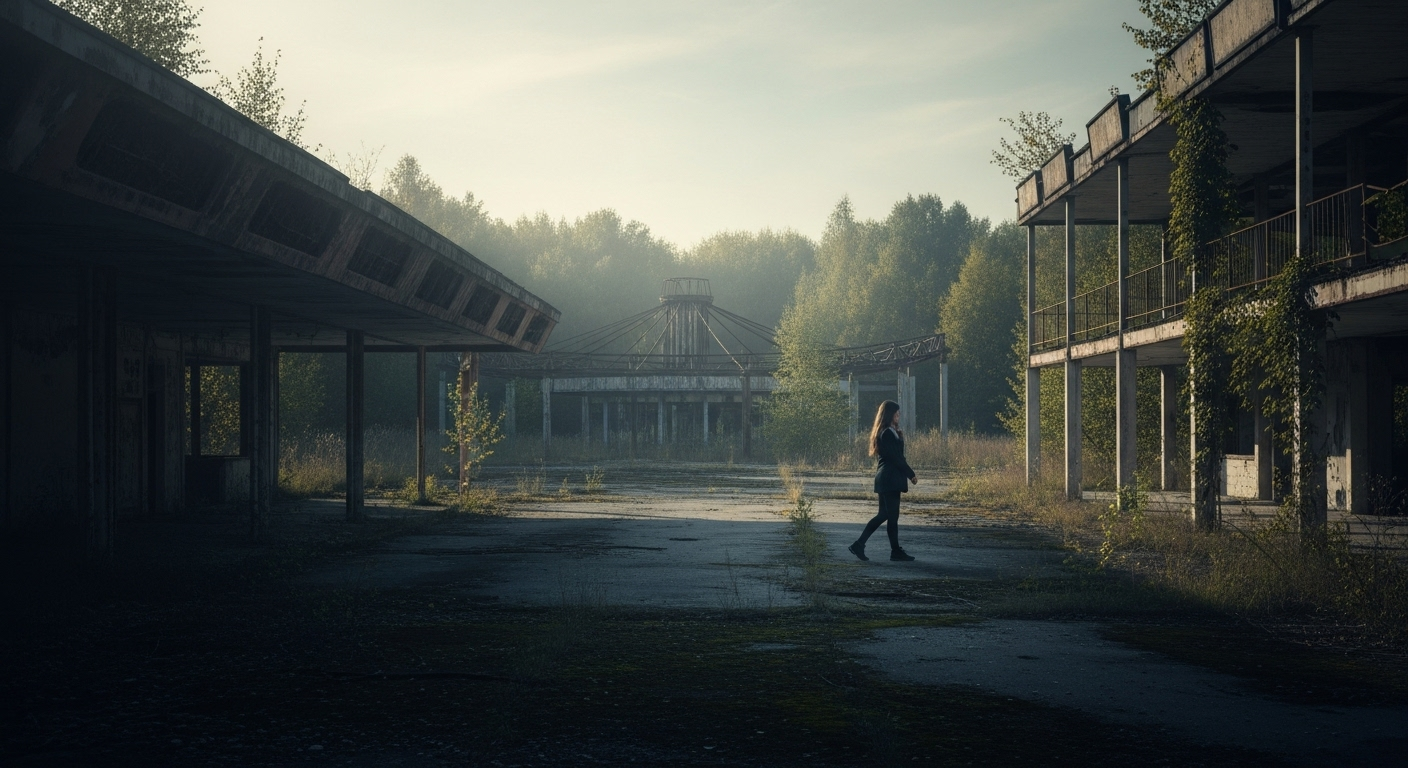
The city of Pripyat in Ukraine, abandoned after the Chernobyl nuclear disaster, attracts thousands of visitors each year.
-
The Hiroshima Peace Memorial in Japan stands as a stark reminder of the horrors of nuclear warfare.
In conclusion, dark tourism represents a fascinating shift in travel trends, reflecting our collective curiosity and our capacity for empathy. While it poses ethical challenges, its potential to educate and evoke reflection is undeniable. With sensitivity and respect, dark tourism can offer a deeply impactful travel experience, bringing us face-to-face with the darker shades of human history.