Read More About Handheld Laser Welding Gun
Handheld laser welding guns are gaining attention for their compact design and ability to support various general welding applications. If you're curious about how they function, where they may be used, or simply want to understand the concept behind this technology, our article provides general awareness-based information without making performance claims. Read more about handheld laser welding gun.
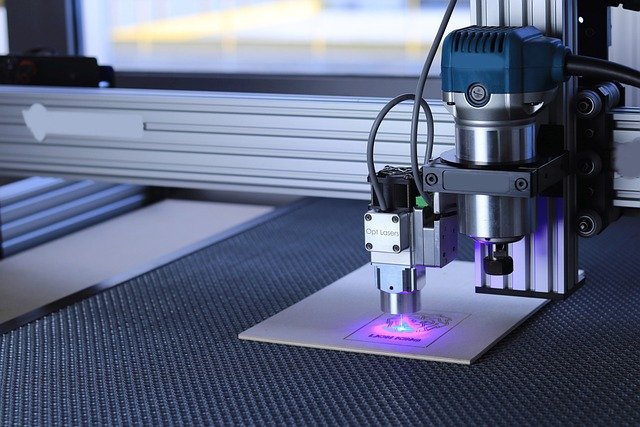

Handheld laser welding guns have revolutionized the welding industry by making high-precision laser welding technology accessible in a portable format. These innovative tools combine the power and accuracy of laser welding with the flexibility and convenience of handheld operation. As manufacturing and repair industries continue to evolve, these devices are gaining recognition for their ability to produce high-quality welds in various settings, from large industrial facilities to smaller workshops and field operations.
What is Handheld Laser Welding Technology?
Handheld laser welding technology represents a significant advancement in portable welding solutions. These devices generate a highly concentrated laser beam that creates a precise heat source for joining metals. Unlike traditional welding methods that use an electric arc or gas flame, laser welding focuses energy into an extremely small area, resulting in minimal heat-affected zones and reduced material distortion.
The core technology relies on fiber laser sources that generate high-powered beams, typically ranging from 1,000 to 1,500 watts for handheld units. These beams are channeled through fiber optic cables to the handheld gun, which contains optics that focus the laser onto the workpiece. Most systems incorporate shielding gas delivery (typically argon) to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, ensuring clean, high-quality welds.
What makes this technology particularly remarkable is its ability to deliver industrial-grade laser welding capabilities in a portable format. The technology has evolved significantly in recent years, with improvements in beam quality, power efficiency, and cooling systems making these tools increasingly practical for a wider range of applications.
Common Applications and Working Mechanisms
Handheld laser welding guns have found applications across numerous industries due to their versatility and precision. In automotive repair, these tools excel at welding thin sheet metal components with minimal distortion. Manufacturing sectors utilize them for joining precision parts, creating seams in enclosures, and performing repair work on high-value components.
The jewelry industry has embraced this technology for intricate repair work and custom fabrication, while metal fabrication shops appreciate the ability to create clean, strong welds without the extensive cleanup required by traditional methods. Additionally, these tools have proven valuable for maintenance and repair operations in facilities where equipment cannot be easily transported to stationary welding stations.
The working mechanism involves a process called keyhole welding, where the intense heat of the laser beam creates a vapor-filled hole in the metal. As the beam moves along the joint, molten metal flows around this keyhole and solidifies behind it, creating a continuous weld seam. Most handheld units operate in pulse mode, allowing precise control over heat input and weld characteristics.
Modern handheld laser welders also incorporate features like adjustable power settings, variable pulse frequencies, and different beam profiles to accommodate various materials and thicknesses. This adaptability makes them suitable for welding everything from thin foils to components several millimeters thick.
Safety Considerations for Handheld Laser Welding
Safety is paramount when operating handheld laser welding equipment due to the potential hazards associated with high-power laser technology. The most significant risk comes from laser radiation, which can cause severe eye damage or blindness if proper protective equipment is not used. Industry-standard protective eyewear specifically designed for the wavelength of the laser being used is essential for operators and anyone in the vicinity.
Skin protection is also crucial, as direct or reflected laser radiation can cause burns. Operators should wear appropriate clothing that covers exposed skin and use gloves designed for laser work. The working environment must be controlled to prevent accidental reflection from shiny surfaces or exposure to bystanders.
Another important safety consideration is fume extraction. The laser welding process can generate metal fumes and particulates that pose respiratory hazards. Proper ventilation or dedicated fume extraction systems should be employed to maintain air quality in the work area. Some advanced systems incorporate built-in extraction directly at the weld point.
Training is perhaps the most critical safety element. Operators must understand not only how to use the equipment effectively but also how to recognize potential hazards and implement appropriate safety protocols. Many jurisdictions require certification for laser equipment operators, and manufacturers typically offer comprehensive training programs for their systems.
Market Perception and Industrial Adoption
The industrial market’s perception of handheld laser welding technology has evolved significantly in recent years. Initially met with skepticism regarding practicality and cost-effectiveness, these tools have increasingly gained acceptance as their capabilities and benefits have become more widely recognized. Industries that value precision, speed, and minimal post-weld processing have been particularly receptive to this technology.
Manufacturing sectors focused on high-value components have been early adopters, appreciating the reduction in distortion and the ability to weld near heat-sensitive components. The automotive industry, especially in repair and restoration work, has embraced the technology for its ability to produce clean welds on thin materials with minimal heat-affected zones.
Market research indicates growing adoption across various industrial sectors, with manufacturers reporting increased interest from small to medium-sized businesses that previously considered laser welding technology out of reach due to cost and complexity. This democratization of laser welding technology represents a significant shift in the welding equipment landscape.
Feedback from industrial users frequently highlights several advantages over traditional welding methods: reduced post-weld cleanup, lower heat input resulting in less distortion, higher precision, and the ability to weld dissimilar metals in some applications. However, challenges remain, including the initial investment cost, the learning curve for operators transitioning from conventional welding methods, and limitations in welding thicker materials compared to traditional processes.
Cost Considerations and Available Equipment
The market for handheld laser welding equipment has expanded significantly, with several manufacturers now offering systems with varying capabilities and price points. Entry-level systems typically start around $25,000 to $30,000, while more advanced models with higher power outputs and additional features can range from $50,000 to $100,000 or more.
| Manufacturer | Model | Power Output | Key Features | Approximate Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPG Photonics | LightWELD | 1500W | Wobble welding, cleaning mode, touchscreen interface | $50,000 - $70,000 |
| Coherent | Manual Laser Welder | 1000W | Compact design, multiple weld modes, integrated cooling | $40,000 - $60,000 |
| Trumpf | TruLaser Weld 1000 | 1000W | Seam tracking, quality monitoring, ergonomic design | $55,000 - $75,000 |
| Raycus | RFL-H1000 | 1000W | Economical design, basic functionality, reliable performance | $25,000 - $45,000 |
| nLIGHT | Corona Portable | 1500W | Advanced beam shaping, high-speed welding, modular design | $60,000 - $80,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Beyond the initial equipment cost, businesses should consider additional factors that influence the total cost of ownership. Consumables such as protective lenses, nozzles, and shielding gas represent ongoing operational expenses. Maintenance requirements, though generally lower than for traditional welding equipment, include periodic calibration and occasional replacement of optical components.
Training costs should also be factored into the investment calculation. Proper operation requires specialized knowledge, and manufacturers typically offer training programs ranging from basic operation to advanced applications. These programs may add several thousand dollars to the initial investment but are essential for safe and effective use of the equipment.
Despite the higher initial investment compared to conventional welding equipment, many businesses report favorable returns due to increased productivity, reduced post-weld processing, and the ability to take on higher-value projects that require superior weld quality and precision.
Conclusion
Handheld laser welding guns represent a significant advancement in welding technology, bringing the precision and quality of laser welding to portable applications. Their ability to produce clean, precise welds with minimal distortion makes them valuable tools across various industries. While safety considerations and initial investment costs present challenges, the technology continues to evolve, becoming more accessible and versatile. As manufacturing processes increasingly demand higher precision and efficiency, handheld laser welding technology is positioned to play an increasingly important role in the future of metal joining and fabrication.